Prioritize...
After completing this section, you should be able to describe absorption, transmission, and scattering as they pertain to electromagnetic radiation passing through a medium.
Read...
Unlike the traveler in Robert Frost's poem, The Road Not Taken, electromagnetic radiation doesn't have much of a choice whenever it encounters objects in its direct path. Indeed, the fate of electromagnetic radiation depends on wavelength and the physical composition of the atoms and molecules in the medium that it is passing through. It is impractical (and impossible) to sort through each atom and molecule in a given object in order to judge its potential effect on the radiation that strikes it ("incident" radiation), so we will consider chunks of matter as whole objects in order to describe their overall effect on incident radiation.
When radiation first encounters some medium (whether it be a collection of gases, a liquid, or a solid), only three things can happen to that radiation:
- transmission -- the radiation passes through the medium unaffected
- absorption -- the radiation "beam" gets extinguished within the medium
- scattering -- the radiation interacts with the medium such that its direction of "travel" changes
In most cases, all three processes can and do occur to some degree. To help you visualize these potential outcomes, check out the brief video (1:59) below:
Click here for a transcript of the video.
When radiation encounters some medium, three things can happen to that radiation. One possibility is that the radiation could pass right through medium unaffected, which is called transmission. Now, 100 percent perfect transmission is pretty rare, except within the vacuum of space. Almost always, there’s at least a little energy that isn’t transmitted through unaffected. An example of a medium with a high transmission value is window glass. Visible light passes through a thin sheet of glass mostly undisturbed, which is why we can see objects clearly on the other side. We call such mediums “transparent” while mediums having low transmission values are called “opaque.” I should point out that the transmission properties of a medium depend on wavelength. An object that is transparent in visible wavelengths might be opaque at infrared wavelengths for example.
The next possibility is called absorption. That’s when the radiation effectively gets extinguished within the medium. When absorption occurs, the radiation is taken up by the matter (typically by the electrons of the atoms) and converted to other forms of energy like heat energy. As with transmission, the amount of energy that an object absorbs depends on the wavelength of the radiation and the physical make-up of the object. For example, freshly fallen snow absorbs little direct sunlight, but snow readily absorbs infrared radiation.
The final possibility is called scattering. That’s when radiation interacts with matter in a way that changes its direction of travel. Scattering can occur in all directions, although some directions are preferred, depending on the size and composition of the particles involved in the scattering event. If the radiation encounters a scattering event and continues on in a forward direction, the event is called "forward-scattering." Likewise, objects can also back-scatter radiation, meaning that they redirect the radiation in all directions back toward the source.
I should point out that I'll sometimes use the word "reflection" as a loose substitute for the "back-scattering" (scattering back toward the radiation source) described in the video, but there's a big difference between this loose use of "reflection" and the classic, pure interpretation of "reflection." Pure reflection means that the angle at which radiation strikes an object must equal the angle at which the radiation is redirected from the object (think about how a billiard ball bounces off a bumper on a pool table). Furthermore, in some rare cases, the scattered radiation may retain the exact same direction that it initially had before the scattering event. When this occurs, the scattered light is counted in the "transmission" category (because it seemingly emerged unchanged from the medium).
Now let's see these processes (particularly absorption and scattering) in action in the atmosphere. First, the atmosphere, like snow (as mentioned in the video), is a highly discriminating absorber (it only absorbs certain wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum). The plot of absorption spectra by various gases (below) indicates how efficiently certain gases and the atmosphere, taken as a whole, absorb various wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. To interpret the graph, note the "0 to 1" scale on the left of the plot, indicating zero percent absorption and 100 percent absorption, respectively. At any specific wavelength, the upward reach of the color shading indicates the percentage of absorption by a particular gas (or the atmosphere, taken as a whole).
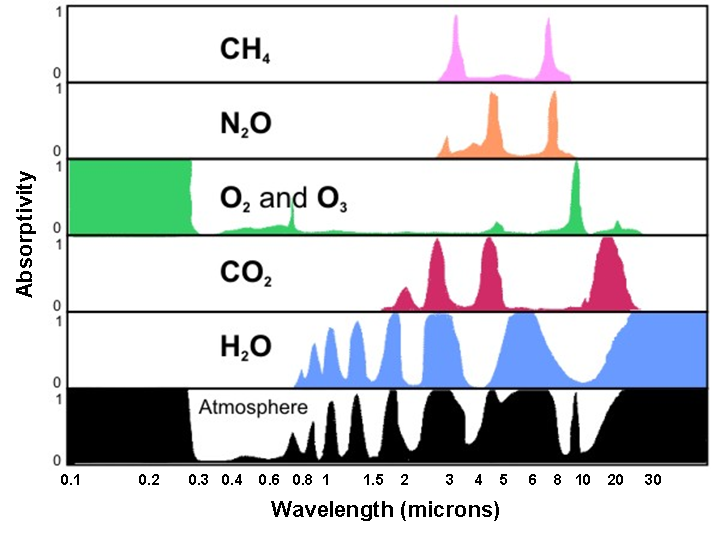
For example, focus your attention on the row for oxygen and ozone, labeled "O2 and O3." Note, to the left of this label, that nearly 100 percent of the radiation emitted at wavelengths ranging from 0.1 to about 0.3 microns is absorbed. Recall that these wavelengths correspond to potentially dangerous ultraviolet radiation emitted by the sun. Ozone, a gas composed of three oxygen atoms (O3), absorbs much of the incoming ultraviolet radiation. Most of this absorption takes place in the stratosphere, which is a layer that spans from 10 to 30 miles above the Earth's surface. Thank goodness for ozone in the stratosphere! Otherwise, cases of skin cancer and other afflictions associated with overexposure to the sun would likely be much more rampant in our society than they actually are.

Scattering, on the other hand, makes things look the way they do. You can't see objects if visible light isn't scattered to your eyes. Check out the great example of scattering on the right. A laser produces a highly focused beam of light waves, all traveling in the same direction. However, since you can see the beam, you know that some of the light is being scattered out of the beam towards the camera lens. This scattering is likely produced by small particles of dust in the air.
I should point out that scattering doesn't have to be a one-time event. Often, radiation will enter an object and encounter many (hundreds or thousands) of scattering events before emerging. This is what happens to make clouds appear white on top and darker on the bottom (cue the obligatory storm photo). It's also what makes snow, salt, sugar, and milk appear white. Furthermore, multiple scattering increases the time that the radiation resides in the medium (as it bounces around, unable to escape). This longer residence time increases the chance that the radiation will also be absorbed by the medium. A great example is the blue hue that ice can take on. Water (even in frozen form) tends to absorb red light at a faster rate than blue light, so over time with multiple scattering events, more blue light is scattered to our eyes (see below)!

Now that we have covered the behavior of the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation and how it travels through space, we need to shift gears and focus on something we ultimately want to measure via remote sensing -- clouds. The detection of clouds by satellites plays a crucial role in weather forecasting. In the next section, we will discuss the four different genres of clouds. By knowing the physical features of these clouds, you will be better prepared to identify specific types of clouds using satellite imagery. Read on.